Does Kratom Interact With Meloxicam (Mobic)?
Kratom and meloxicam can interact in two ways and could cause some side effects.
Always talk to your physician before starting these two.
Kratom Can Increase Meloxicam’s Effects (Agonistic Interaction)
Kratom and meloxicam can have a mild to moderate agonistic interaction. Both work as pain relievers, and taking them together could cause an increase in their overall effects. That might sound like a good thing, but it usually isn’t. Increasing the potency of a drug also increases the likelihood of severe side effects.
Kratom binds to opioid receptors in the body, effectively decreasing pain, improving mood, and relieving anxiety. However, it also inhibits COX 1 and 2 [7].
In the same way, meloxicam works by inhibiting COX 1 and 2, with its effect being more on COX-2. This allows it to decrease inflammation and pain.
Using these two drugs together can potentiate the analgesic effect. While it could help relieve pain, it can also cause more side effects like excessive sleepiness, stomach issues, and dizziness.
Slowed Elimination of Meloxicam (Metabolic Inhibition)
When two drugs that require the same enzymes for their metabolism are taken together, they can compete to bind to such enzymes. This phenomenon is known as metabolic inhibition and can slow the drug’s elimination from the body.
Kratom is metabolized by the cytochrome enzymes of the liver, namely CYP3A4, CYP2D6, and CYP2C9 [1].
On the other hand, meloxicam is metabolized by CYP2C9 and CYP3A4 [2].
Taking them together could cause the two drugs to compete for the metabolic enzymes, slowing their metabolism and elimination. If the drugs last in the system for longer than expected, it increases the chances of experiencing side effects.
Because NSAIDs can harm the gastrointestinal tract, meloxicam could produce stomach symptoms ranging from abdominal pain to perforation if its metabolism is delayed.
Kratom & Meloxicam (Mobic) Interactions
Meloxicam belongs to the drug class of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). These drugs treat inflammatory conditions and decrease pain. They work by acting on the cyclooxygenase receptors and preventing the action of prostaglandins in the body. Combining kratom with other NSAIDS will have similar risks.
Other NSAIDS that can interact with kratom include:
- Aspirin (Ascriptin, Aspergum, Entercote)
- Acetaminophen (Tylenol)
- Ibuprofen (Motrin, Advil, Nuprin, Caldolor & Neoprofen)
- Celecoxib (Celebrex & Onsenal)
- Naproxen (Aleve)
- Ketorolac (Toradol)
- Etodolac (Ultradol)

Is It Safe to Take Kratom With Meloxicam (Mobic)?
Consuming kratom with meloxicam can cause mild to moderate reactions. Taking them together could cause an excess in their pain-relieving effects and also slow down their elimination from the body. There could be increased effects such as dizziness, sleepiness, sedation, and vomiting.
As NSAIDs can be dangerous for the gastrointestinal tract, a delay in its metabolism could cause meloxicam to cause gastric symptoms ranging from abdominal pain to gastric perforation.
Take these drugs only after checking with your physician. Never take them on your own. Also, if you suffer any unusual side effects, seek medical help right away.
What is Meloxicam (Mobic)?
Meloxicam is a painkiller belonging to the nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDS) class. It is used in pain management for osteoarthritis in adults, rheumatoid arthritis in adults, and juvenile rheumatoid arthritis in the pediatric age group.
It can treat pain caused by musculoskeletal conditions, osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, and treatment of dental or post-surgical pain. It is a good choice for those who require once-daily dosing because it has a longer half-life than most other NSAIDs. Meloxicam can be used orally, transdermally, or intravenously. It is a selective COX-2 inhibitor that may reduce the likelihood of gastrointestinal side effects.
Details & Specifications
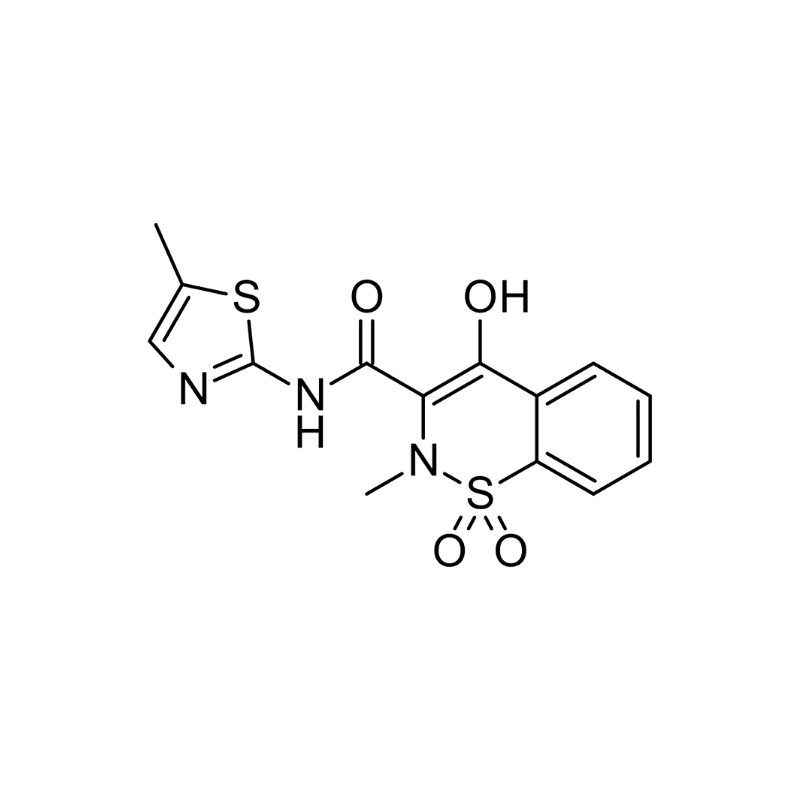
| Drug Name | Meloxicam |
| Trade name | Anjeso, Mobic, Qmiiz, Vivlodex |
| Classification | Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs |
| CYP Metabolism | CYP2C9, CYP3A4 |
| Interaction With Kratom | Metabolic inhibition, agonistic interaction |
| Risk of Interaction | Moderate |
What is Meloxicam (Mobic) Used for?
Thanks to their analgesic, anti-inflammatory, and antipyretic properties, cyclooxygenase (COX) inhibitors like meloxicam have a wide variety of indications, including:
Pain & Inflammation Treatment
Meloxicam is often used to treat pain and inflammation [2]. Meloxicam inhibits the enzyme cyclooxygenase (COX), which converts arachidonic acid to prostaglandin H2 — the first step in manufacturing the inflammatory mediators, prostaglandins. Meloxicam has been demonstrated to selectively inhibit COX-2 over COX-1, especially at low therapeutic dosages.
This process results in a decrease in prostaglandin production, which causes severe inflammatory symptoms. Prostaglandins activate neuronal pain receptors, inhibiting their production and providing analgesic and anti-inflammatory benefits.
Osteoarthritis Pain Management
Meloxicam is helpful in the treatment of osteoarthritic (OA) pain. It can also help improve patient performance and has minimal side effects if used for a short time.
A study showed that 12 weeks of treatment with meloxicam decreased pain symptoms significantly in 774 patients with confirmed OA of the hip or knee [3]. It can also help manage postoperative pain in users who underwent total knee arthroplasty for knee OA [4].
Rheumatoid Arthritis Treatment
Meloxicam is effective in the treatment of pain caused due to rheumatoid arthritis. At 7.5 to 15 mg daily, meloxicam is as effective as diclofenac, piroxicam, and naproxen as an anti-inflammatory and analgesic [5].
Juvenile Rheumatoid Arthritis Treatment
Meloxicam is also helpful in treating juvenile rheumatoid arthritis. In one study, 36 patients with juvenile rheumatoid arthritis were prescribed meloxicam; the pain decreased significantly with improved symptoms [6].

What’s the Dose of Meloxicam (Mobic)?
The recommended dose of meloxicam is 7.5 to 15 mg orally per day. However, doctors may change the dose depending on the patient’s needs.
Generic & Brand Name Versions
- Anjeso
- Mobic
- Qmiiz
- Vivlodex

What Are the Side Effects of Meloxicam (Mobic)?
Although well-tolerated by most patients, meloxicam and other COX inhibitors can cause several side effects, including:
- Abdominal pain
- Anemia
- Angina
- Congestive heart failure
- Constipation
- Diarrhea
- Dizziness
- Edema
- Gastrointestinal hemorrhage
- Gastrointestinal perforation
- Headache
- Hepatitis
- Hypertension
- Indigestion
- Inflammation of the digestive tract
- Myocardial infarction
- Nausea
- Upper respiratory infection
- Vomiting
What is Kratom?
Kratom is a herbal extract derived from the leaves of the Mitragyna speciosa tree, a Southeast Asian tropical tree belonging to the coffee family. It’s native to Thailand, Indonesia, Malaysia, Myanmar, and Papua New Guinea, where it’s been used in herbal medicine for a long time.
Kratom has opioid characteristics as well as stimulating qualities. Low doses of kratom work as a stimulant, while the higher doses work as a sedative.
Kratom leaves can be chewed or made into powder, which can be used in many ways.
It relieves anxiety and chronic pain and also helps treat opioid withdrawal. A long term use can induce addiction and withdrawal symptoms in the users.

What’s Kratom Used for?
Long ago, farmers and working people in Southeast Asia used kratom to combat fatigue and relieve pain. Today, kratom has various indications, including:
What is the Dose of Kratom?
The dose of kratom varies depending on the effects you want. The amount ranges from 2 to 12 g, but users adjust it according to their needs.
If you’re using kratom for energy, mood, or focus, stick with lower doses — usually 2-5 g. If you need pain relief or a good night’s sleep, go with more significant amounts — between 6-12 g.
Start with lower doses and only increase if necessary.
Related: Kratom Dosage Guide and Calculator

What Are the Side Effects of Kratom?
While kratom is safe, there are side effects. These are usually minor and don’t cause long-term issues. They’re also more likely to be an issue with higher doses, so if you experience any of them, try cutting back on how much you take.
- Anxiety
- Arrhythmias
- Dizziness
- Constipation
- Drowsiness
- Dry mouth
- Frequent urination
- Irritability
- Itching
- Liver damage
- Loss of appetite
- Nausea
- Vomiting
Kratom addiction is a possibility but unlikely if proper precautions are in place. Use as little as possible and take breaks from it to decrease the risk.
Related: Is Kratom Safe?
What Are the Different Types of Kratom?
Because of the many kratom strains, kratom can be challenging to buy. Many people are overwhelmed by the choices. Here’s the rundown of what you need to know.

White Vein Kratom
White vein kratom enhances cognitive performance, increasing mental attention, vitality, and overall mood. The leaves of this plant are harvested before they reach full maturity, changing the alkaloid content. White vein kratom’s qualities are similar to those of caffeine.

Red Vein Kratom
Red vein kratom comes from a fully ripe kratom leaf. Compared to other types of kratom, this type has a balanced alkaloid profile, causing it to have a diverse range of effects and making it highly effective in treating body aches.
It also contains sedative abilities and also helps in relaxing the body. Red vein kratom has an extra function as an energy booster and increases alertness and attention. Its calming effect helps to treat anxiety.

Green Vein Kratom
Green vein kratom comes from leaves with an average level of maturity. This level is considered ideal, with all its properties at their maximum. The effects may be mild compared to other kinds of kratom, but it is long-lasting.
It has a stimulating and revitalizing effect. When consumed in large doses, it might create high levels of pleasure. It also helps people stay calm and increases their focus.

Yellow Vein Kratom
Yellow vein kratom can also help increase vigor while lessening anxiety’s effects. The yellow attribute is due to it being a form of white vein kratom whose colors changed due to the drying process. It delivers pain relief and improves attention.
Key Takeaways: Is it Safe to Mix Kratom & Meloxicam (Mobic)?
You could experience mild to moderate side effects from mixing kratom and meloxicam. This combination could cause increased sedating effects, a slowdown in the drugs’ metabolization, and an increased risk of dangerous side effects such as oversedation and gastric perforation.
So don’t start taking kratom and meloxicam together on your own. Always consult your prescribing physician first.
- Kamble, S. H., Sharma, A., King, T. I., León, F., McCurdy, C. R., & Avery, B. A. (2019). Metabolite profiling and identification of enzymes responsible for the metabolism of mitragynine, the major alkaloid of Mitragyna speciosa (kratom). Xenobiotica, 49(11), 1279-1288.
- Ludwig, E., Schmid, J., Beschke, K., & Ebner, T. (1999). Activation of human cytochrome P-450 3A4-catalyzed meloxicam 5′-methylhydroxylation by quinidine and hydroquinidine in vitro. Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics, 290(1), 1-8.
- Fleischmann, R., Iqbal, I., & Slobodin, G. (2002). Meloxicam. Expert opinion on pharmacotherapy, 3(10), 1501-1512.
- Yocum, D., Fleischmann, R., Dalgin, P., Caldwell, J., Hall, D., Roszko, P., & Meloxicam Osteoarthritis Investigators. (2000). Safety and efficacy of meloxicam in the treatment of osteoarthritis: a 12-week, double-blind, multiple-dose, placebo-controlled trial. Archives of internal medicine, 160(19), 2947-2954.
- Hu, F., Wu, G., Zhao, Q., & Wu, J. (2021). Evaluation of analgesic effect, joint function recovery and safety of meloxicam in knee osteoarthritis patients who receive total knee arthroplasty: A randomized, controlled, double-blind study. Medicine, 100(35).
- Ahmed, M., Khanna, D., & Furst, D. E. (2005). Meloxicam in rheumatoid arthritis. Expert opinion on drug metabolism & toxicology, 1(4), 739-751.
- Foeldvari, I., Burgos-Vargas, R., Thon, A., & Tuerck, D. (2002). High response rate in phase I/II study of meloxicam in juvenile rheumatoid arthritis. The Journal of Rheumatology, 29(5), 1079-1083.
- Utar, Z., Majid, M. I. A., Adenan, M. I., Jamil, M. F. A., & Lan, T. M. (2011). Mitragynine inhibits the COX-2 mRNA expression and prostaglandin E2 production induced by lipopolysaccharide in RAW264. 7 macrophage cells. Journal of Ethnopharmacology, 136(1), 75-82.